Optical Encoder
1. Optical encoder
An optical encoder is a sensor used to detect the rotation angle and position of an axis. It senses the rotation of the axis and detects the rotational speed, amount, and direction, outputting this information as electrical signals.They are widely used in scenes that require precise control, such as the internal components of assembly robots and conveyors used in factories, automatic doors, and familiar devices such as copiers in offices.
2. Basic technology of Optical encoder
2-1. Optical encoder
An optical encoder creates light intensity variations by placing a movable slit and a fixed slit between a light-emitting element and a light-receiving element. The light-receiving element converts this into a electric signal strength, which is then waveform-shaped by electronic circuits and output as a rectangular pulse or sin cycle signal that corresponds to the amount of movement of the slit. This sensor can be used to control the rotation of an axis in rotary encoders or to control the movement of an object in linear encoders.
An optical encoder creates light intensity variations by placing a movable slit and a fixed slit between a light-emitting element and a light-receiving element. The light-receiving element converts this into a electric signal strength, which is then waveform-shaped by electronic circuits and output as a rectangular pulse or sin cycle signal that corresponds to the amount of movement of the slit. This sensor can be used to control the rotation of an axis in rotary encoders or to control the movement of an object in linear encoders.
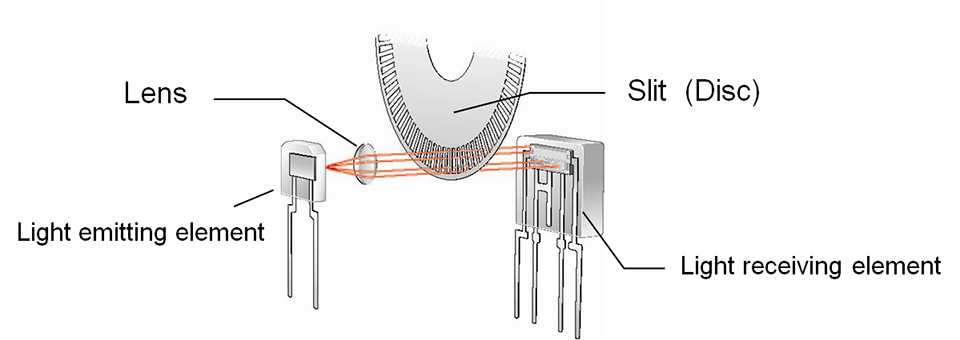 Fig.1. Optical system of transmissive type encoder
Fig.1. Optical system of transmissive type encoder
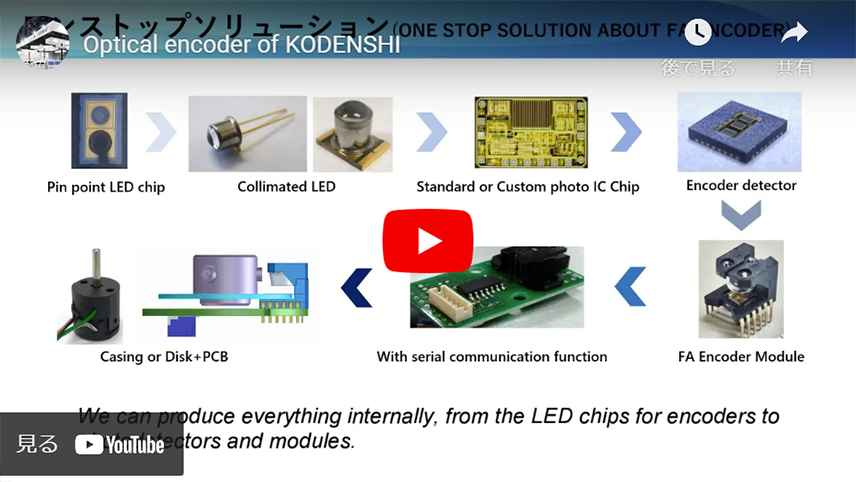
At Kodenshi, we have the capability to achieve end-to-end in-house production, from circuit design for the photodetector to package assembly. We can produce everything internally, from the LED chips for encoders to photodetectors and modules.
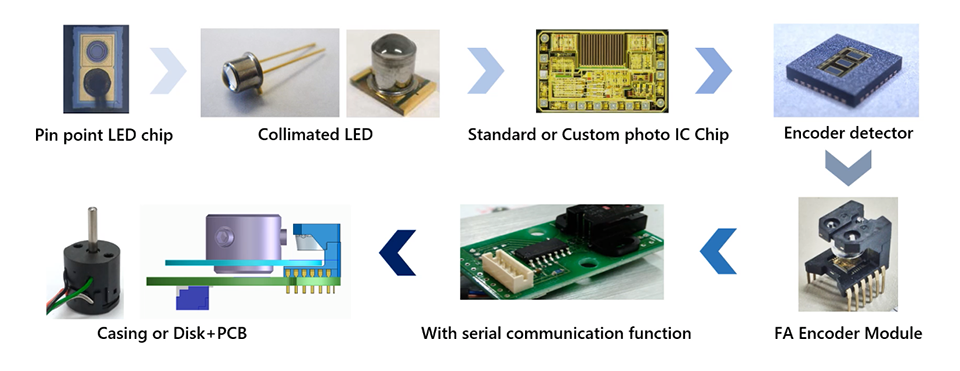 Fig.2. End-to-end in-house production
Fig.2. End-to-end in-house production
2-2. Encoder element device
An optical encoder consists of a photodetector and an emitter. We are developing high-intensity and highly reliable Pin-point-LEDs as shown in Fig.3. it is an LED that has a small emitting part in a dot shape. For sensors performing precise measurements, a smaller diameter of the emitting part in the light source is advantageous.
An optical encoder consists of a photodetector and an emitter. We are developing high-intensity and highly reliable Pin-point-LEDs as shown in Fig.3. it is an LED that has a small emitting part in a dot shape. For sensors performing precise measurements, a smaller diameter of the emitting part in the light source is advantageous.
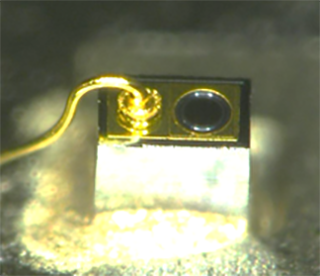 Fig.3. Pin point LED
Fig.3. Pin point LED
Fig.4 shows the collimated light LEDs. When designing the optical system of the encoder, it is desirable for the light to propagate in a parallel path. However, standard LEDs exhibit radial emission patterns. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain parallel light by placing a collimate lens in the optical path. KODENSHI have developed collimated light LEDs with high parallel light characteristics by optimization of lens design.
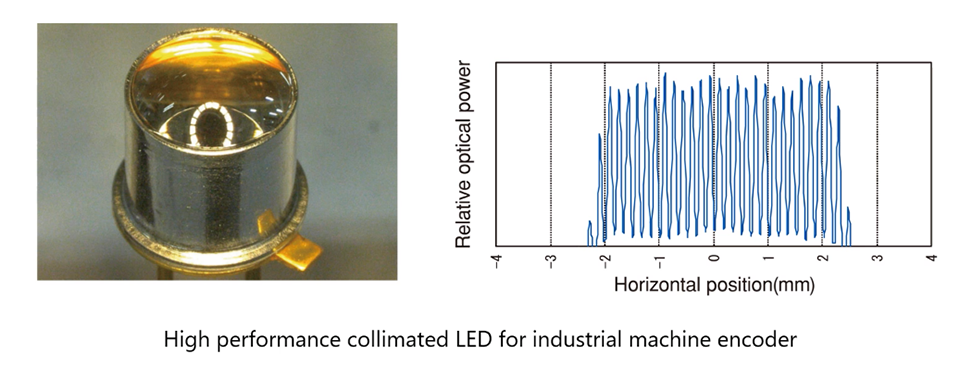 Fig.4. Collimated light LED
Fig.4. Collimated light LED
Additionally, we are also developing and manufacturing the photodetectors for encoders as shown in Fig.5.
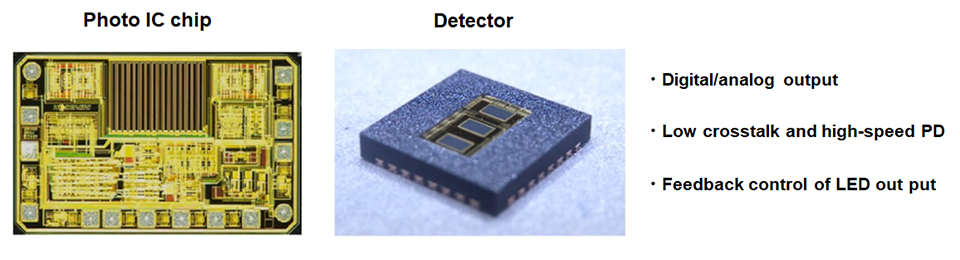 Fig.5. Photodetectors for encoders
Fig.5. Photodetectors for encoders
3. Application
Encoders are widely used in scenes that require precise control, such as the internal components of assembly robots and conveyors used in factories, automatic doors, and familiar devices suchi as copiers in offices.
 Fig.6. Widely used in scenes
Fig.6. Widely used in scenes
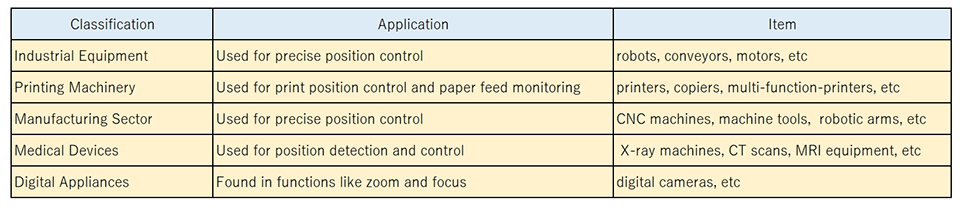
Table1 Encoder applications

4. Encoder Type
In this section, we will introduce Kodenshi's optical encoders, transmissive type encoders, reflective encoders, and FA encoders.
For more detailed product information, please click here.
4-1. Transmissive type encoder
Transmissive type encoders, in which the light-emitting and light-receiving elements are arranged opposite each other as shown in Fig.7. It is one of the most versatile products, offering a wide range of variations. For more detailed product information, please click here.
Transmissive type encoders, in which the light-emitting and light-receiving elements are arranged opposite each other as shown in Fig.7. It is one of the most versatile products, offering a wide range of variations. For more detailed product information, please click here.
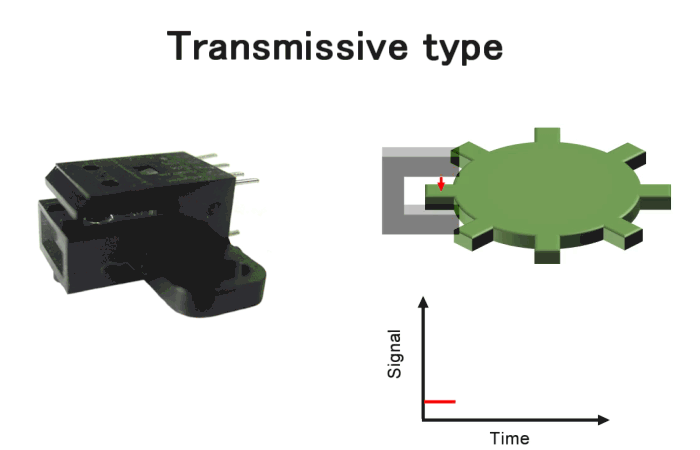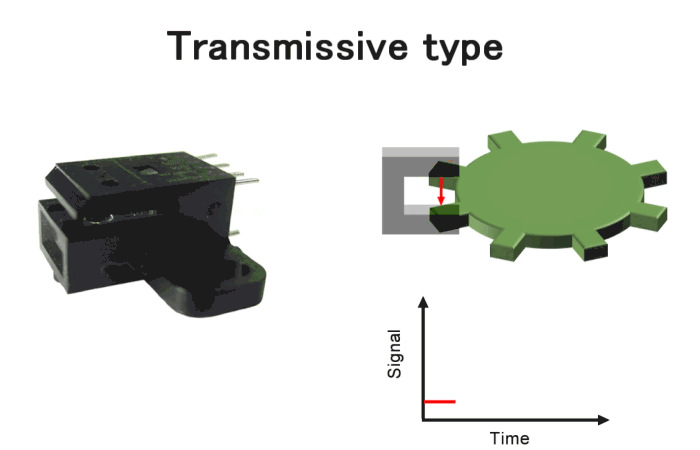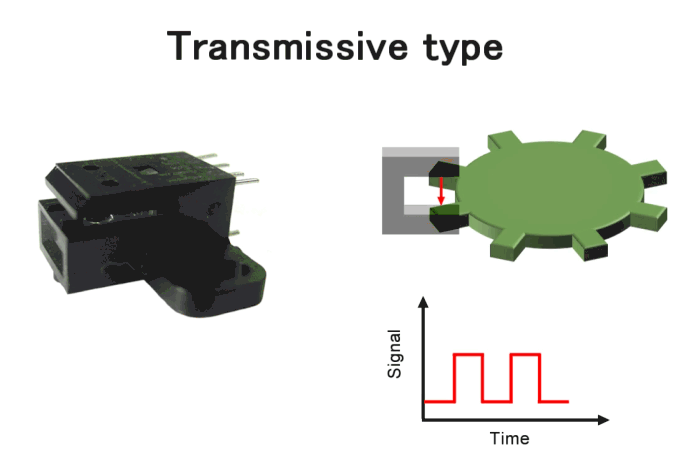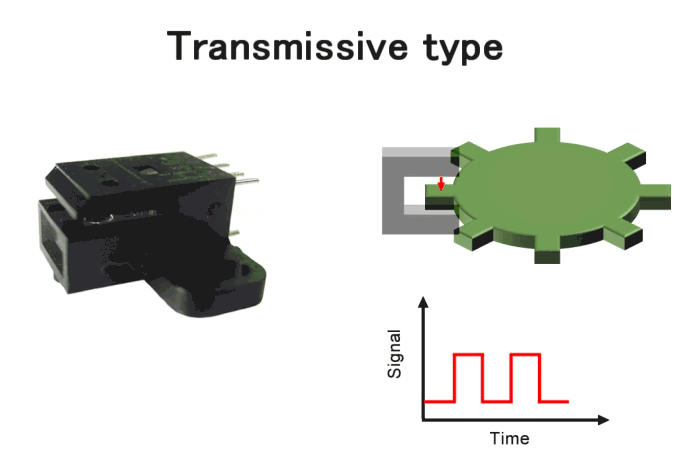 Fig.7. Transmissive type encoders
Fig.7. Transmissive type encoders
Features
2ch type
- Incremental encoder
- Resolution: 18 LPI~1200 LPI
3ch type
- This is an encoder that can detect specific positions, such as the origin position, in addition to rotation speed and direction.
- Incremental encoder
- Resolution: 150 LPI, 300 LPI, 360 LPI
4-2. FA Encoder
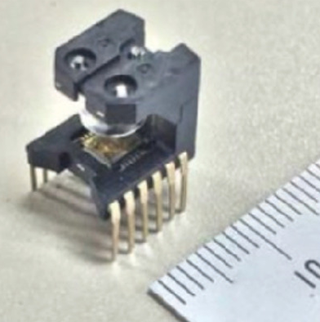 Fig.8. FA Encoder
Fig.8. FA Encoder
FA encoder
This is an encoder that outputs the required 6-channel signals for the operation of a servomotor and includes built-in multiplication and LED light amount correction circuit.
Feature
- 6 ch
- Incremental encoder
- Resolution: 150 LPI, 300 LPI, 360 LPI
4-3. Reflective encoder
Typically, optical encoders have transmissive type optical configuration. In this configuration, the disk is positioned between the light emitter and the light receiver. On the other hand, in reflective encoders, the light beam emitted from the light emitter reflects off the disk and enters the light receiver. As a result, reflective encoders can be significantly compact size as shown in Fig.9.
Typically, optical encoders have transmissive type optical configuration. In this configuration, the disk is positioned between the light emitter and the light receiver. On the other hand, in reflective encoders, the light beam emitted from the light emitter reflects off the disk and enters the light receiver. As a result, reflective encoders can be significantly compact size as shown in Fig.9.
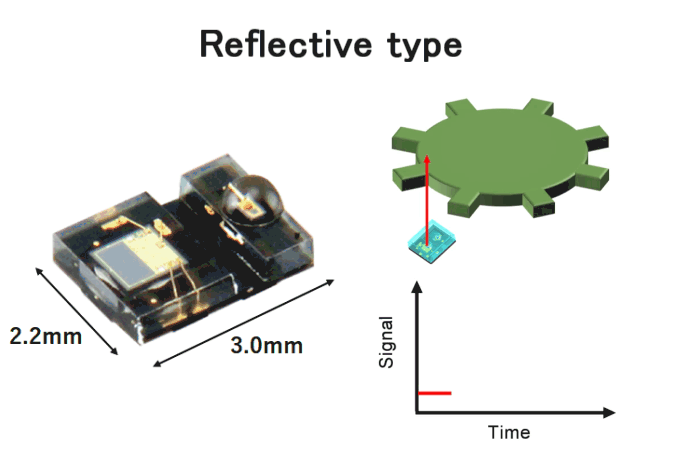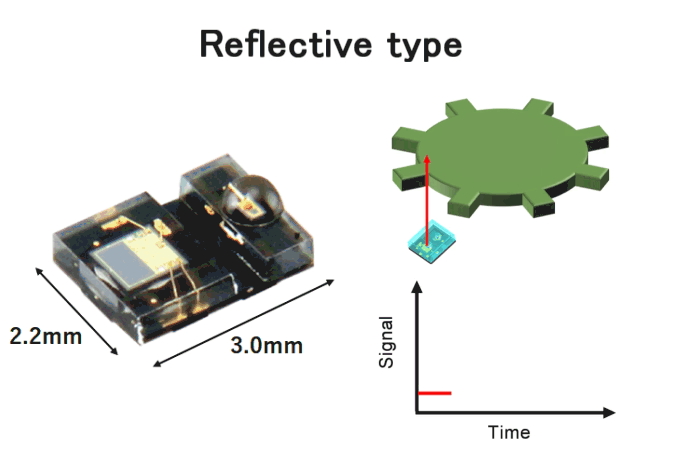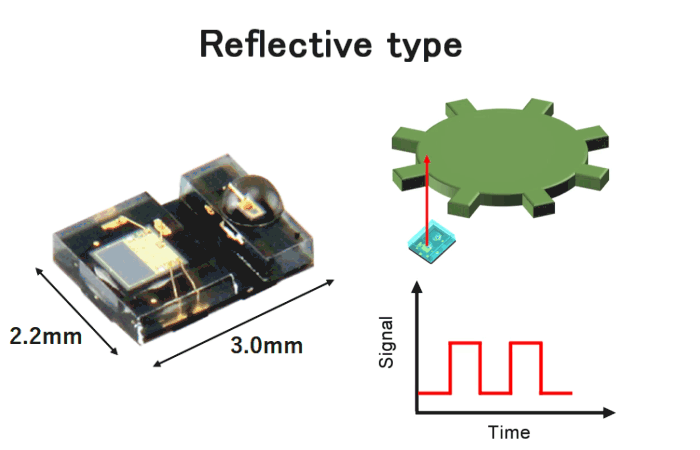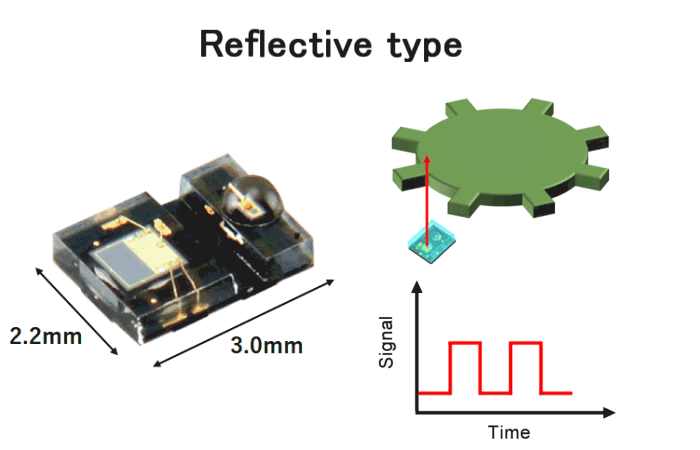 Fig.8. Reflective encoder
Fig.8. Reflective encoder
Features
- Small outline size 2.2×3.0×1.1mm
- Incremental encoder
- A phase/B phase 2ch digital output
4-4. Reflective encoder module
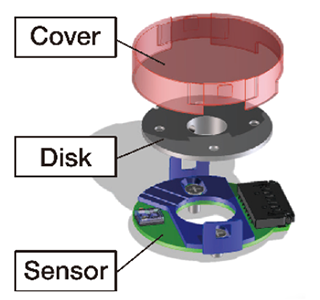 Fig.9. Reflective encoder module
Fig.9. Reflective encoder module
Reflective encoder module
This is a module that includes the necessary components such as a disk and hub for the operation of the encoder. Using a reflective encoder, it is compact and high-performance. By attaching it to the motor shaft with a jig, it can be quickly operated as an encoder.
Feature
- Size : φ30×6.5㎜
- This can be attached to φ8 Shaft
- 2ch incremental digital encoder
- Inclusing Disk and Hub
- Number of counts : 512, 1024 CRP
Inquiry